Appendix P – Mixed phase
and ice crystal icing envelope (Deep convective clouds)
ED Decision 2015/008/R
The ice crystal icing envelope is depicted in Figure 1 below.
Figure 1 –
Convective Cloud Ice Crystal Envelope
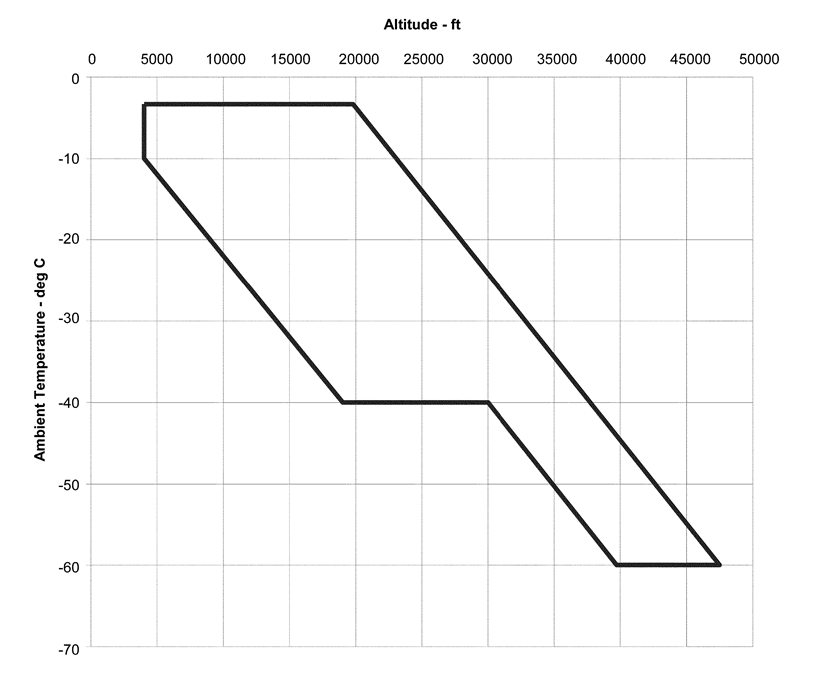
Within the envelope, total water content (TWC) in
g/m3 has been determined based upon the adiabatic lapse defined by the
convective rise of 90 % relative humidity air from sea level to higher
altitudes and scaled by a factor of 0.65 to a standard cloud length of 32.2 km
(17.4 nautical miles). Figure 2 displays TWC for this distance over a range of
ambient temperature within the boundaries of the ice crystal envelope
specified in Figure 1.
Figure
2 – Total Water Content
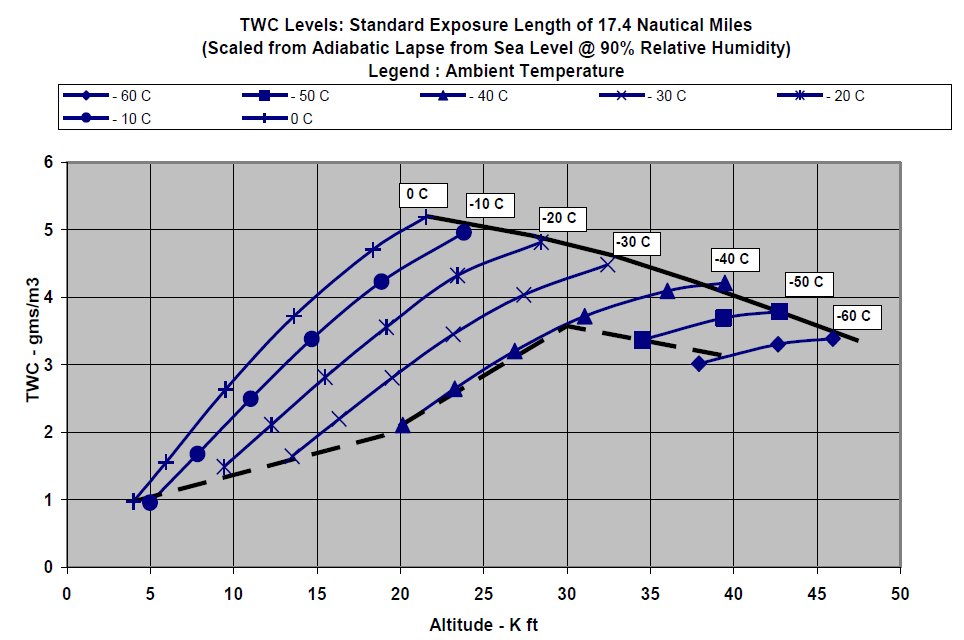
Ice crystal size median mass dimension (MMD) range is 50–200 microns (equivalent spherical size) based upon measurements near convective storm cores. The TWC can be treated as completely glaciated (ice crystal) except as noted in the Table 1.
Table 1 –
Supercooled Liquid Portion of TWC
|
Temperature
range – deg C |
Horizontal
cloud length |
LWC – g/m3 |
|
0 to -20 |
≤92.6 km (50 nautical miles) |
≤1.0 |
|
0 to -20 |
Indefinite |
≤0.5 |
|
< -20 |
|
0 |
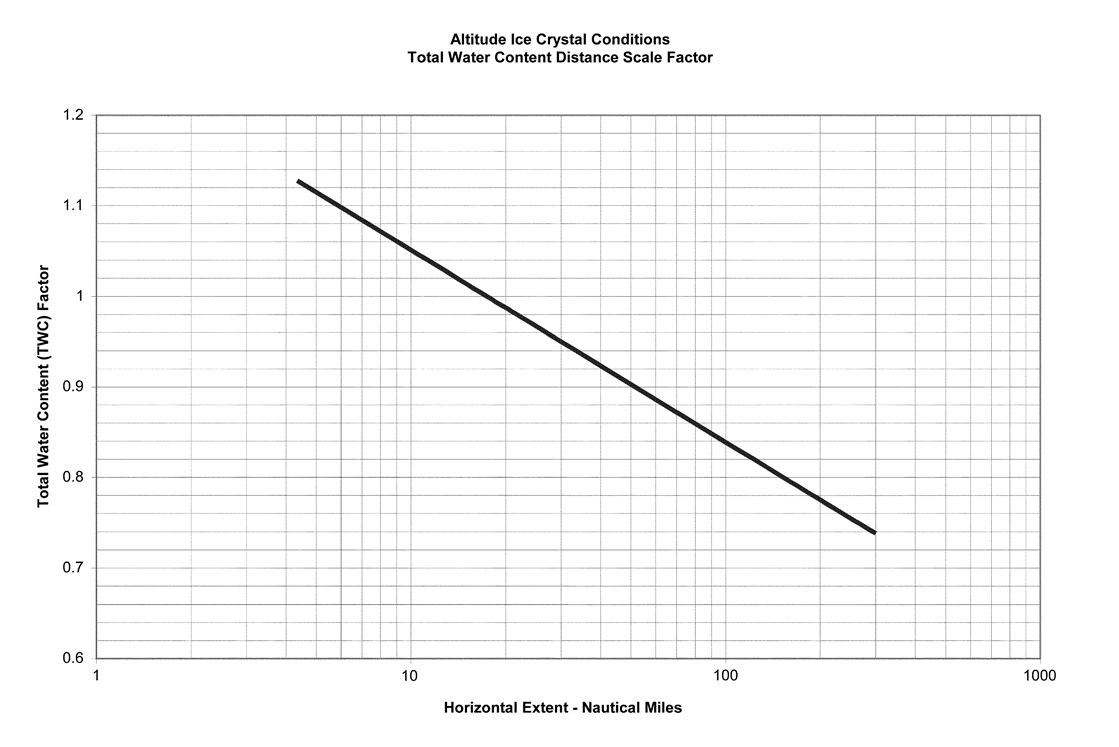
The TWC levels displayed in Figure 2 represent TWC values for a standard exposure distance (horizontal cloud length) of 32.2 km (17.4 nautical miles) that must be adjusted with length of icing exposure.
Figure
3 – Exposure Length Influence on TWC
[Amdt 25/16]