AMC1
ATCO.D.010(a) Composition of initial training
ED Decision 2023/011/R
GENERAL
1. Structure of the basic and rating training syllabi
(a) The basic and rating training syllabi have been structured as follows:
(1) The syllabus is divided into subjects, which are divided into topics that are in turn divided into subtopics. This structure serves the definition and classification of the objectives. There can be one or several objectives linked to each subtopic.
(2) Objectives are assigned to a specific subject which deals with the knowledge and skills needed to accomplish the related subject objective.
(3) Subjects, topics and subtopics are contained in Appendices 2 to 8 to Annex I to Commission Regulation (EU) 2015/340, and are repeated in:
— AMC1 ATCO.D.010(a)(1) Composition of initial training — BASIC TRAINING — SUBJECT OBJECTIVES AND TRAINING OBJECTIVES;
— AMC1 ATCO.D.010(a)(2)(i) Composition of initial training — AERODROME CONTROL VISUAL RATING (ADV) TRAINING — SUBJECT OBJECTIVES AND TRAINING OBJECTIVES;
— AMC1 ATCO.D.010(a)(2)(ii) Composition of initial training — AERODROME CONTROL INSTRUMENT RATING FOR TOWER ADI (TWR) TRAINING — SUBJECT OBJECTIVES AND TRAINING OBJECTIVES;
— AMC1 ATCO.D.010(a)(2)(iii) Composition of initial training — APPROACH CONTROL PROCEDURAL RATING (APP) TRAINING — SUBJECT OBJECTIVES AND TRAINING OBJECTIVES;
— AMC1 ATCO.D.010(a)(2)(iv) Composition of initial training — AREA CONTROL PROCEDURAL RATING (ACP) TRAINING — SUBJECT OBJECTIVES AND TRAINING OBJECTIVES;
— AMC1 ATCO.D.010(a)(2)(v) Composition of initial training — APPROACH CONTROL SURVEILLANCE RATING (APS) TRAINING — SUBJECT OBJECTIVES AND TRAINING OBJECTIVES
— AMC1 ATCO.D.010(a)(2)(vi) Composition of initial training — AREA CONTROL SURVEILLANCE RATING (ACS) TRAINING — SUBJECT OBJECTIVES AND TRAINING OBJECTIVES
in order to provide the reader with a comprehensive and unique reference document for the basic and each of the rating trainings. Subject objectives and training objectives are included in and form an integral part of each of the aforementioned AMC.
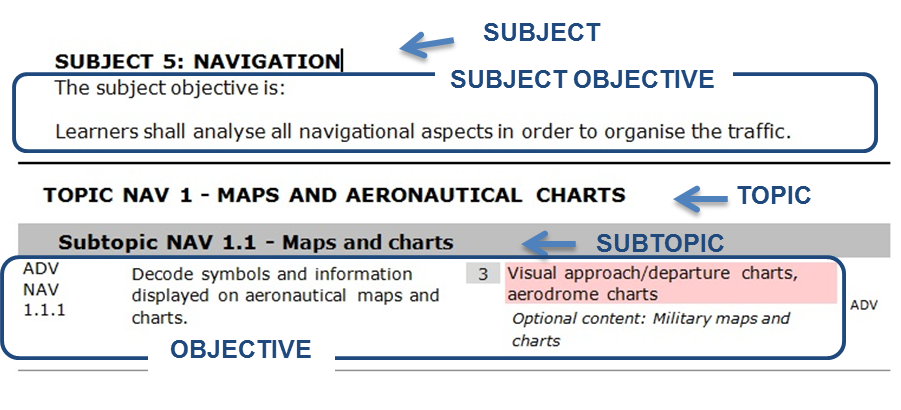
Figure
1: Layout of the syllabus
[applicable until 3 August 2024 - ED Decision
2019/023/R]
GENERAL
1. Structure
of the basic and rating training syllabi
(a) The
basic and rating training syllabi are structured as follows:
(1) The
syllabus is divided into subjects, which are divided into topics that are in
turn divided into subtopics. This structure serves the definition and
classification of the objectives. There can be one or several objectives
linked to each subtopic.
(2) Objectives
are assigned to a specific topic/subtopic which deals with the knowledge and
skills needed to accomplish the related subject.
(3) Subjects,
topics and subtopics are contained in Appendices 2 to 7 to Annex I to
Commission Regulation (EU) 2015/340, and are repeated in:
—
AMC1 ATCO.D.010(a)(1) Composition of initial training — BASIC TRAINING — TRAINING
OBJECTIVES;
—
AMC1 ATCO.D.010(a)(2)(i) Composition of initial training — AERODROME CONTROL
RATING (ADC) TRAINING — TRAINING OBJECTIVES;
—
AMC1 ATCO.D.010(a)(2)(ii) Composition of initial training — APPROACH CONTROL
PROCEDURAL RATING (APP) TRAINING — TRAINING OBJECTIVES;
—
AMC1 ATCO.D.010(a)(2)(iii) Composition of initial training — AREA CONTROL
PROCEDURAL RATING (ACP) TRAINING — TRAINING OBJECTIVES;
—
AMC1
ATCO.D.010(a)(2)(iv)
Composition of initial training — APPROACH CONTROL SURVEILLANCE RATING (APS)
TRAINING — TRAINING OBJECTIVES
—
AMC1 ATCO.D.010(a)(2)(v) Composition of initial training — AREA CONTROL
SURVEILLANCE RATING (ACS) TRAINING — TRAINING OBJECTIVES
in order to provide the reader with a
comprehensive and unique reference document for the basic and each of the
rating training courses. Training objectives are included in, and form an
integral part of, each of the aforementioned AMC.

Figure 1: Layout of the syllabus
[applicable from 4 August 2024 - ED
Decision 2023/011/R]
(b) The following principles may be applied to the development of a training course that is based on any of the syllabi:
(1) The structure of the syllabi and the order of the objectives contained therein is neither intended to convey a pedagogical sequence nor to indicate a relative level of importance.
(2) No objective from the basic training syllabus is repeated as ‘a refresher’ in the rating training syllabi.
(3) The number of objectives contained within a subtopic does not necessarily signify how long it should take to teach that subtopic. For example, a subtopic containing five relatively straightforward objectives may take a shorter time to be taught than another subtopic containing two complex objectives.
2. Structure of the objectives
(a) An objective consists of three elements:
(1) The corpus, which is a description of the required performance. It always contains an action verb to ensure that the outcome is observable. The action verb is always associated with a defined taxonomy.
(2) The level, which indicates numerically the taxonomy of the action verb.
(3) The content, which may be implicit or explicit. The explicit content is written in the content field, while the implicit content is not but, instead, is implied in the corpus of the objective and other elements (syllabus, subject, etc.). Content that is a required part of the objective is written in the red-shaded field. Optional content, written in italics, may be used if considered appropriate.
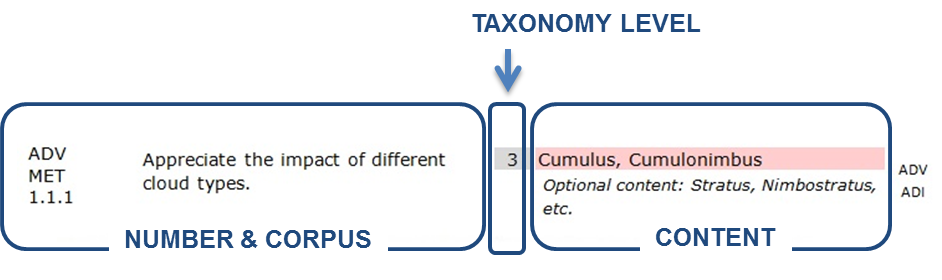
Figure
2: Layout of an objective
[applicable until 3 August 2024 - ED Decision
2019/023/R]
(3) The
content, which may be implicit or explicit. Explicit content is written in the
content field, while implicit content is not but, instead, is implied in the
corpus of the objective and other elements (syllabus, subject, etc.). Content
that is a required part of the objective is written in the red-shaded field.
Optional content, written in italics is provided to help training designers
develop their training material and may suggest possible reference documents
that could be used and/or elaborate on the content with specific examples.
With or without explicit content, the objective needs to be covered since the
implementation is implied in its corpus (text of the objective) and associated
context (Subtopic/Topic/Subject/ Rating).
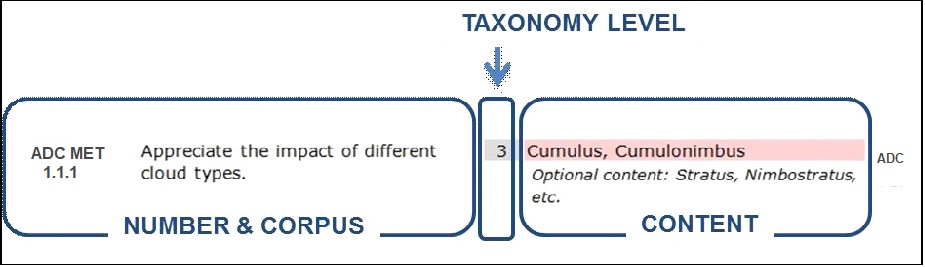
Figure 2: Layout of an objective
[applicable from 4 August 2024 - ED
Decision 2023/011/R]
3. Repeated and common objectives
(a) Repeated and common objectives are only applicable to rating training.
(b) To the right of each objective, there is an indication of which other ratings contain this particular objective. If the rating is indicated in red italics, it notifies the reader that the objective(s) is (are) verbatim in each rating; however, the objective numbers are different. This indication is the first step to help the training providers identify the potential commonalities between the various syllabi. As a second step, the training provider must determine, at the level of local implementation, whether the objective is to be regarded as repeated or common.
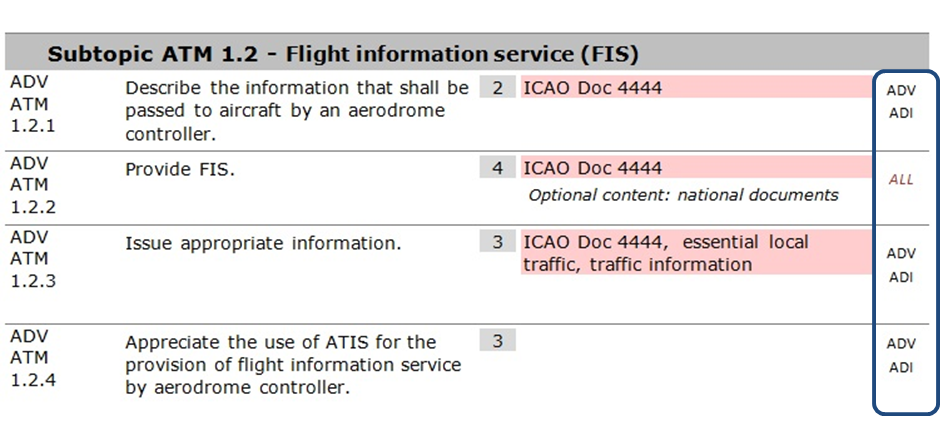
Figure
3: Indication of the ratings that particular objective applies to
[applicable until 3 August 2024 - ED Decision
2019/023/R]
(b) To
the right of each objective, there is an indication of which other ratings
contain this particular objective. If the rating is indicated in red italics,
it notifies the reader that the objective(s) is (are) verbatim in each rating;
however, the objective numbers are different. This indication is the first
step to help training providers identify potential commonalities between the
various syllabi. As a second step, training providers must determine, on the
level of local implementation, whether the objective is to be regarded as
repeated or common.
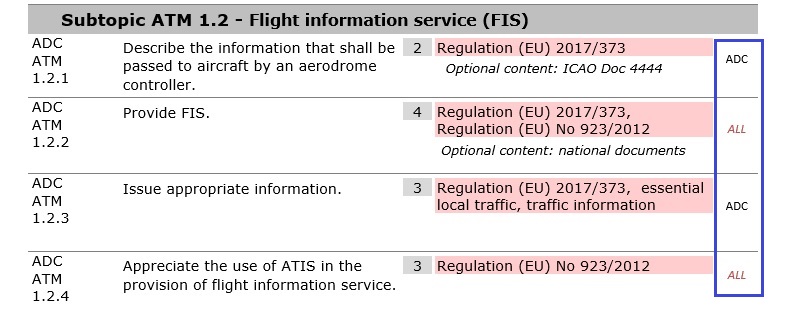
Figure 3: Indication of the ratings
to which a particular objective applies
[applicable from 4 August 2024 - ED
Decision 2023/011/R]
3.1 Repeated
objectives
All the objectives appearing in a syllabus are implicitly appropriate to this syllabus. As a consequence, objectives may be repeated ‘verbatim’ in different rating syllabi and nevertheless specify a different performance. The reader always needs to mentally add the sentence ‘in this syllabus context’ at the end of each objective.
For example, the objective ‘use approved
phraseology’ is repeated (same level, same corpus, same content) in all the
syllabi but is different because the context is different in each syllabus (a
learner that is able to use approved phraseology for en-route traffic will
need additional training before mastering the phraseology in the provision of
aerodrome control).
3.2 Common
objectives
(a) Common objectives are verbatim the same objectives that appear in more than one rating syllabi in the same context so that they do not need to be taught again in case of combined or successively organised courses.
For example, the objective ‘describe the human
information-processing model’ is common for all the syllabi because the
context is non-specific and is, therefore, not determined by the type of
rating.
(b) As a general principle, the rating subject ‘Human Factors’ is identical in each of the rating training syllabi and can be considered as containing common objectives because the context is always the same. This means that the rating training objectives relating to Human Factors need to be taught only once. If a learner acquires an additional rating, that learner would not be required to repeat the Human Factors objectives.
4. Action verbs that support the taxonomy for training objectives
(a) The five taxonomy levels should be understood to have the following levels of complexity:
(1) Action verbs for Level 1
Level 1 — A basic knowledge of the subject. It is the ability to remember essential points, to memorise data and retrieve it.
|
L1 Verb |
Definition |
Example |
|
Define |
State what it is and what its limits are; state the definition. |
Define ATC service. |
|
Draw |
Produce a picture, pattern or diagram. |
Draw the block diagram. Draw a holding pattern. |
|
List |
Say one after the other. |
List the main structure components of an aircraft. |
|
Name |
Give name of objects or procedures. |
Name the components of an ILS. Name the key national and international aviation organisations. |
|
Quote |
Repeat what is written or said. |
Quote ICAO definition of ATC service. |
|
Recognise |
To know what it is because you have seen it before. |
Recognise the
information contained in the different parts of the |
|
State |
Say or write in a formal or definite way. |
State the meteorological hazards to aviation. |
[applicable until 3 August 2024 - ED Decision
2019/023/R]
(1) Action verbs for Level 1
Level 1 — A basic knowledge of the subject.
It is the ability to remember essential points, to memorise data and retrieve
it.
|
L1 Verb |
Definition |
Example |
|
Define |
State what it is and
what its limits are; state the definition. |
Define ATC service. |
|
Draw |
Produce a picture,
pattern or diagram. |
Draw the block
diagram. Draw a holding
pattern. |
|
List |
Say one after the
other. |
List the different
types of jet engines. |
|
Name |
Give the name of
objects or procedures. |
Name the competent
authorities responsible for ATCO licensing and ANSP oversight. |
|
Quote |
Repeat what is written
or said. |
Quote the ICAO
definition of ATC service. |
|
Recognise |
To know what it is
because you have seen it before. |
Recognise the
information contained in the different parts of the |
|
State |
Say or write in a
formal or definite way. |
State the
meteorological hazards to aviation. |
[applicable from 4 August 2024 - ED
Decision 2023/011/R]
(2) Action verbs for Level 2
Level 2 — The ability to understand and to discuss the subject matter intelligently in order to represent and act upon certain objects and events.
|
L2 Verb |
Definition |
Example |
|
Characterise |
To describe the quality of features in something. |
Characterise the main items of ATC equipment. |
|
Consider |
To think carefully about it. |
Consider the benefits of Critical Incident Stress Management (CISM). |
|
Demonstrate |
Describe and explain; logically or mathematically prove the truth of a statement. |
Demonstrate the importance of good communication in ATC. |
|
Describe |
Say what it is like or what happened. |
Describe the methods by which ICAO notifies and implements legislation. |
|
Differentiate |
Show the differences between things. |
Differentiate between different types of visibility. |
|
Explain |
Give details about something or describe so that it can be understood. |
Explain the purpose and function of ICAO. |
|
Take account of |
Take into consideration before deciding. |
Take account of the wind influence when calculating a ground speed. Take account of the limitations of equipment and systems. |
[applicable until 3 August 2024 - ED Decision
2019/023/R]
(2) Action verbs for Level 2
Level 2 — The ability to understand and to
discuss the subject matter intelligently in order to represent and act upon
certain objects and events.
|
L2 Verb |
Definition |
Example |
|
Characterise |
To describe the
quality of features in something. |
Characterise the main
radio navigation techniques based on ground-based systems. |
|
Consider |
To think carefully
about it. |
Consider how the
evolution of a situation may have an impact on safety. |
|
Demonstrate |
Describe and explain;
logically or mathematically prove the truth of a statement. |
Demonstrate the
importance of good communication in ATC. |
|
Describe |
Say what it is like or
what happened. |
Describe the methods
by which ICAO notifies and implements legislation. |
|
Differentiate |
Show the differences between
things. |
Differentiate between
different types of visibility. |
|
Explain |
Give details about
something or describe so that it can be understood. |
Explain the purpose
and function of ICAO. |
|
Take account of |
Take into
consideration before deciding. |
Take account of the
limitations of equipment and systems. |
[applicable from 4 August 2024 - ED
Decision 2023/011/R]
(3) Action verbs for Level 3
Level 3 — A thorough knowledge of the subject and the ability to apply it with accuracy. The ability to make use of the repertoire of knowledge to develop plans and activate them.
|
L3 Verb |
Definition |
Example |
|
Act |
Carry out, execute. |
Act to reduce stress. |
|
Apply |
Use something in a situation or activity. |
Apply separation. |
|
Appreciate |
To understand a situation and know what is involved in a problem-solving situation, to state a plan without applying it. |
Appreciate the necessity for coordination (the learner says that the coordination will be done and with whom; the learner does not perform the actual coordination). |
|
Assist |
Help somebody to do a job by doing part of it. |
Assist the pilot. |
|
Calculate |
To discover from information you already have by arithmetic; to think about a possible cause of action in order to form an opinion or decide what to do. |
Calculate appropriate levels. Calculate conversions between the three north designations. |
|
Check |
Make sure the information is correct (satisfactory). |
Check the accuracy of flight data information. Check availability of information material. |
|
Choose |
Select out of number, decide to do one thing rather than another. |
Choose appropriate levels. Choose which aircraft should be vectored. |
|
Collect |
Assemble, accumulate, bring or come together. |
Collect examples of different types of error, their causes and consequences for ATC. |
|
Conduct |
Organise and carry out. |
Conduct coordination. |
|
Confirm |
Establish more firmly, corroborate. |
Confirm sequence order. |
|
Decode |
Turn into ordinary writing, decipher. |
Decode the content of weather reports and forecast. |
|
Encode |
Put into code or cipher. |
Encode and decode flight plans (including supplementary information). |
|
Estimate |
Form an approximate judgement of a number, form an opinion. |
Estimate distance and direction between two points. |
|
Execute |
Perform action. |
Execute corrective actions. |
|
Extract |
Copy out, make extracts from, find, deduce. |
Extract pertinent data from relevant sources to produce a flight progress display. |
|
Identify |
Associate oneself inseparably with, establish the identity. |
Identify
the role of ATC as a service provider and the requirements of the Identify an aircraft. |
|
Inform |
Tell, give facts or information. |
Inform supervisor of situation. |
|
Initiate |
Begin, set going, originate. |
Initiate appropriate coordination. |
|
Input |
Enter in the system. |
Input data. |
|
Issue |
Send forth, publish. |
Issue appropriate ATC clearances. Issue appropriate traffic information. |
|
Maintain |
Cause or enable to continue. |
Maintain flight data display. |
|
Measure |
Ascertain extent or quality of (thing) by comparison with fixed unit or with object of known size. |
Measure distance on a map. |
|
Monitor |
Keep under observation. |
Monitor traffic. Monitor the effect of human information-processing factors on decision-making. |
|
Notify |
Make known, announce, report. |
Notify runway in use. |
|
Obtain |
Acquire easily without research. |
Obtain meteorological information. Obtain information from the relieving controller. |
|
Operate |
Conduct work on equipment. |
Operate the equipment of the controller working position. |
|
Pass |
Move, cause to go, transmit. |
Pass essential traffic information without delay. |
|
Perform |
Carry into effect, go through, execute. |
Perform communication effectively. |
|
Process |
To put through the steps of a prescribed procedure. |
Process pertinent data on data displays. |
|
Record |
Register, set down for remembrance or reference. |
Record information by writing effectively. |
|
Relay |
Receive and pass on, broadcast. |
Relay meteorological information from pilot reports. |
|
Respond |
Provide an answer, perform answering or corresponding action. |
Respond to loss/doubt concerning identification. Respond to distress and urgency messages and signals. |
|
Scan |
Continuously observe rapidly, sequentially and selectively in order to extract relevant data. |
Scan data display. |
|
Transfer |
Hand over. |
Transfer information to the relieving controller. |
|
Update |
Refresh, bring up to date. |
Update the data display to accurately reflect the traffic situation. |
|
Use |
Employ for a purpose, handle as instrument, put into operation. |
Use approved phraseology. Use the available means for coordination. |
|
Verify |
Establish truth of. |
Verify the mode C information. |
[applicable until 3 August 2024 - ED Decision
2019/023/R]
(3) Action
verbs for Level 3
Level 3 — A thorough knowledge of the
subject and the ability to apply it with accuracy. The ability to make use of
the repertoire of knowledge to develop plans and activate them.
|
L3 Verb |
Definition |
Example |
|
Act |
Carry out, execute. |
Act to reduce stress. |
|
Apply |
Use something in a situation or activity. |
Apply separation. |
|
Appreciate |
To understand a situation and know
what is involved in a problem-solving situation, to state a plan without
applying it. |
Appreciate the need for coordination
(the learner says that the coordination will be done and with whom; the
learner does not perform the actual coordination). |
|
Assist |
Help somebody to do a job by doing
part of it. |
Assist the pilot. |
|
Calculate |
To discover from information you
already have by arithmetic; to think about a possible cause of action in
order to form an opinion or decide what to do. |
Calculate appropriate levels. Calculate conversions between the
three north designations. |
|
Check |
Make sure the information is correct
(satisfactory). |
Check all relevant documentation
before managing traffic. Check availability of information. |
|
Choose |
Select out of number, decide to do one
thing rather than another. |
Choose appropriate levels. Choose the appropriate separation
methods. |
|
Collect |
Assemble, accumulate, bring or come
together. |
Collect appropriate information
relevant to the situation. |
|
Conduct |
Organise and carry out. |
Conduct level changes. |
|
Confirm |
Establish more firmly, corroborate. |
Confirm sequence order. |
|
Decode |
Turn into ordinary writing, decipher. |
Decode the content of weather reports
and forecasts. |
|
Encode |
Put into code or cipher. |
Encode and decode flight plans
(including supplementary information). |
|
Estimate |
Form an approximate judgement of a
number, form an opinion. |
Estimate the heading for a new track
and the distance to the next way point. |
|
Execute |
Perform action. |
Execute selected plan in a timely
manner. |
|
Extract |
Copy out, make extracts from, find,
deduce. |
Extract pertinent data from relevant
sources to produce a flight progress display. |
|
Identify |
Associate oneself inseparably with,
establish the identity. |
Identify potential or actual abnormal
and emergency situations. Identify aircraft. |
|
Inform |
Tell, give facts or information. |
Inform the supervisor of local factors
affecting the ATS system capacity and air traffic flow management. |
|
Initiate |
Begin, set going, originate. |
Initiate appropriate coordination. |
|
Input |
Enter in the system. |
Input data. |
|
Issue |
Send forth, publish. |
Issue appropriate ATC clearances. Issue appropriate information
concerning the position of conflicting traffic. |
|
Maintain |
Cause or enable to continue. |
Maintain situational awareness by
monitoring traffic |
|
Measure |
Ascertain extent or quality of (thing)
by comparison with fixed unit or with object of known size. |
Measure distance on a map. |
|
Monitor |
Keep under observation. |
Monitor the technical integrity of the
controller working position. |
|
Notify |
Make known, announce, report. |
Notify runway in use. |
|
Obtain |
Acquire easily without research. |
Obtain meteorological information. |
|
Operate |
Conduct work on equipment. |
Operate the equipment of the
controller working position. |
|
Pass |
Move, cause to go, transmit. |
Pass essential traffic information
without delay. |
|
Perform |
Carry into effect, go through,
execute. |
Perform communication effectively. |
|
Process |
To put through the steps of a
prescribed procedure. |
Process pertinent data on data
displays. |
|
Record |
Register, set down for remembrance or
reference. |
Record information by writing
effectively. |
|
Relay |
Receive and pass on, broadcast. |
Relay meteorological information. |
|
Respond |
Provide an answer, perform answering
or corresponding action. |
Respond to loss/doubt concerning
identification. Respond to distress and urgency
messages and signals. |
|
Scan |
Continuously observe rapidly,
sequentially and selectively in order to extract relevant data. |
Scan data display. |
|
Transfer |
Hand over. |
Transfer information to the relieving
controller. |
|
Update |
Refresh, bring up to date. |
Update the data display to accurately
reflect the traffic situation. |
|
Use |
Employ for a purpose, handle as
instrument, put into operation. |
Use approved phraseology. Use the available means for
coordination. |
|
Verify |
Establish truth of. |
Verify that the settings of the
working position are appropriate. |
[applicable from 4 August 2024 - ED
Decision 2023/011/R]
(4) Action verbs for Level 4
Level 4 — Ability to establish a line of action within a unit of known applications following the correct chronology and the adequate method to resolve a problematic situation. This involves the integration of known applications in a familiar situation.
|
L4 Verb |
Definition |
Example |
|
Acquire |
Gain by oneself and for oneself, obtain after research. |
Acquire relevant aeronautical information. |
|
Adjust |
Change to a new position, value or setting. |
Adjust the surveillance system display. |
|
Allocate |
Assign, devote. |
Allocate levels (height, altitude, flight level) according to altimetry data. |
|
Analyse |
Examine minutely the constitution of. |
Analyse examples of pilot–controller communication for effectiveness. Analyse the information provided by the radar equipment. |
|
Assign |
Designate or set an element. |
Assign codes. |
|
Coordinate |
Negotiate with others in order to work together effectively. |
Coordinate runway in use. Coordinate when providing FIS. |
|
Comply |
Act in accordance with. |
Comply with rules. |
|
Delegate |
Commit authority to somebody. |
Delegate separation to pilots in the case of aircraft executing successive visual approaches. |
|
Detect |
Discover existence of. |
Detect potential conflict. |
|
Ensure |
Make safe, make certain. |
Ensure the agreed course of action is carried out. |
|
Expedite |
Assist the progress of, do speedily. |
Expedite traffic. |
|
Integrate |
Combine into a whole, complete by addition of parts. |
Integrate appropriate ATC clearances in control service. |
|
Manage |
Handle, conduct, maintain control over something, be in charge of. |
Manage traffic on the manoeuvring area. Manage traffic in accordance with procedural changes. |
|
Organise |
Give orderly structure to, frame and put into working order. |
Organise pertinent data on data displays. Organise priority of actions. |
|
Predict |
Forecast. |
Predict positions of aircraft in the aerodrome traffic and taxi circuits. |
|
Provide |
Supply, furnish. |
Provide radar separation. Provide FIS. |
|
Relate |
Establish link with. |
Relate a pressure setting to an altitude. |
[applicable until 3 August 2024 - ED Decision
2019/023/R]
(4) Action
verbs for Level 4
Level 4 — Ability to establish a line of
action within a unit of known applications following the correct chronology
and the adequate method to resolve a problematic situation. This involves the
integration of known applications in a familiar situation.
|
L4 Verb |
Definition |
Example |
|
Acquire |
Gain by oneself and for oneself,
obtain after research. |
Acquire relevant aeronautical
information. |
|
Adjust |
Change to a new position, value or
setting. |
Adjust the surveillance system
display. |
|
Allocate |
Assign, devote. |
Allocate levels according to altimetry
data. |
|
Analyse |
Examine minutely the constitution of. |
Analyse examples of pilot–controller
communication for effectiveness. Analyse the information provided by
the ATS surveillance system. |
|
Assign |
Designate or set an element. |
Assign codes. |
|
Coordinate |
Negotiate with others in order to work
together effectively. |
Coordinate runway in use. Coordinate when providing FIS. |
|
Comply |
Act in accordance with. |
Comply with rules. |
|
Delegate |
Commit authority to somebody. |
Delegate separation to pilots in the
case of aircraft executing successive visual approaches. |
|
Detect |
Discover existence of. |
Detect conflicts in time for
appropriate resolution. |
|
Ensure |
Make safe, make certain. |
Ensure the agreed course of action is
carried out. |
|
Expedite |
Assist the progress of, do speedily. |
Expedite traffic. |
|
Integrate |
Combine into a whole, complete by
addition of parts. |
Integrate appropriate ATC clearances
in control service. |
|
Manage |
Handle, conduct, maintain control over
something, be in charge of. |
Manage traffic on the manoeuvring
area. Manage traffic in accordance with a
change to operational procedures. |
|
Organise |
Give orderly structure to, frame and
put into working order. |
Organise pertinent data on data
displays. Organise priority of actions. |
|
Predict |
Forecast. |
Predict positions of aircraft in the
aerodrome traffic and taxi circuits. |
|
Provide |
Supply, furnish. |
Provide vectoring. Provide FIS. |
|
Relate |
Establish link with. |
Relate a pressure setting to an
altitude. |
[applicable from 4 August 2024 - ED
Decision 2023/011/R]
(5) Action verbs for Level 5
Level 5 — Ability to analyse new situation in order to elaborate and apply one or other relevant strategy to solve a complex problem. The defining feature is that the situation is qualitatively different from those previously met, requiring judgement and evaluation of options.
|
L5 verb |
Definition |
Example |
|
Assess |
Estimate value or difficulty, evaluate, appraise. |
Assess workload. |
|
Balance |
Weigh (a question, two arguments, etc., against each other). |
Balance the workload with the traffic demand. |
|
Discuss |
Investigate by reasoning or argument. |
Discuss the impact of regulation. |
|
Evaluate |
Ascertain amount of, find numerical expression for. |
Evaluate the necessary information to be provided to pilots in need of navigational assistance. |
|
Interpret |
To decide on something's meaning or significance when there is a choice. |
Interpret operational information. |
|
Optimise |
To make optimal; get the most out of; use best; modify to achieve maximum efficiency. |
Optimise the use of support tools. |
|
Resolve |
Solve, clear up, settle. |
Resolve conflict. |
|
Select |
Pick out as best or most suitable. |
Select the runway in use. |
|
Theorise |
Extract general principles from a particular experience. |
Theorise the resolution of conflict between a slow and a fast aircraft. |
|
Validate |
Make valid, ratify, prove valid, show or confirm the validity of something. |
Validate one radar vectoring option to expedite the traffic. |
[applicable until 3 August 2024 - ED Decision
2019/023/R]
(5) Action
verbs for Level 5
Level 5 — Ability to analyse new
situation in order to elaborate and apply one or other relevant strategy to
solve a complex problem. The defining feature is that the situation is
qualitatively different from those previously met, requiring judgement and
evaluation of options.
|
L5 verb |
Definition |
Example |
|
Assess |
Estimate value or difficulty,
evaluate, appraise. |
Assess workload. |
|
Balance |
Weigh (a question, two arguments,
etc., against each other). |
Balance the workload against personal
capacity. |
|
Discuss |
Investigate by reasoning or argument. |
Discuss the impact of regulation. |
|
Evaluate |
Ascertain amount of, find numerical
expression for. |
Evaluate the necessary information to
be provided to pilots in need of navigational assistance. |
|
Interpret |
To decide on something’s meaning or
significance when there is a choice. |
Interpret operational information. |
|
Optimise |
To make optimal; get the most out of; use
best; modify to achieve maximum efficiency. |
Optimise the use of support tools. |
|
Resolve |
Solve, clear up, settle. |
Resolve conflict. |
|
Select |
Pick out as best or most suitable. |
Select the runway in use. |
|
Theorise |
Extract general principles from a particular
experience. |
Theorise the resolution of conflict
between a slow and a fast aircraft. |
|
Validate |
Make valid, ratify, prove valid, show
or confirm the validity of something. |
Validate one radar vectoring option to
expedite the traffic. |
[applicable from 4 August 2024 - ED
Decision 2023/011/R]
(b) Application of taxonomy levels to practically based objectives
(1) Objectives at taxonomy level 3 or higher, which are of a practical nature, related to all subjects except ATM, may be achieved by any suitable type of practical training methods, e.g. hands-on, plotting on charts, etc.
(2) Objectives at taxonomy level 3 or higher, for the ATM subject (basic and rating), are practical by nature and require the integration of several knowledge areas and skills at the same time, e.g. vectoring of an aircraft requires knowledge and skills in the areas of radiotelephony, aircraft performance, navigation and radar theory. Therefore, ATM level 3 objectives should be achieved through the use of a part-task trainer or a simulator.
(3) ATM level 4 objectives should be achieved for the most part through the use of a simulator. A part-task trainer, which presents operational situations at an enforced pace, may be used to achieve some ATM level 4 objectives.
(4) ATM level 5 objectives should be achieved through the use of a simulator.